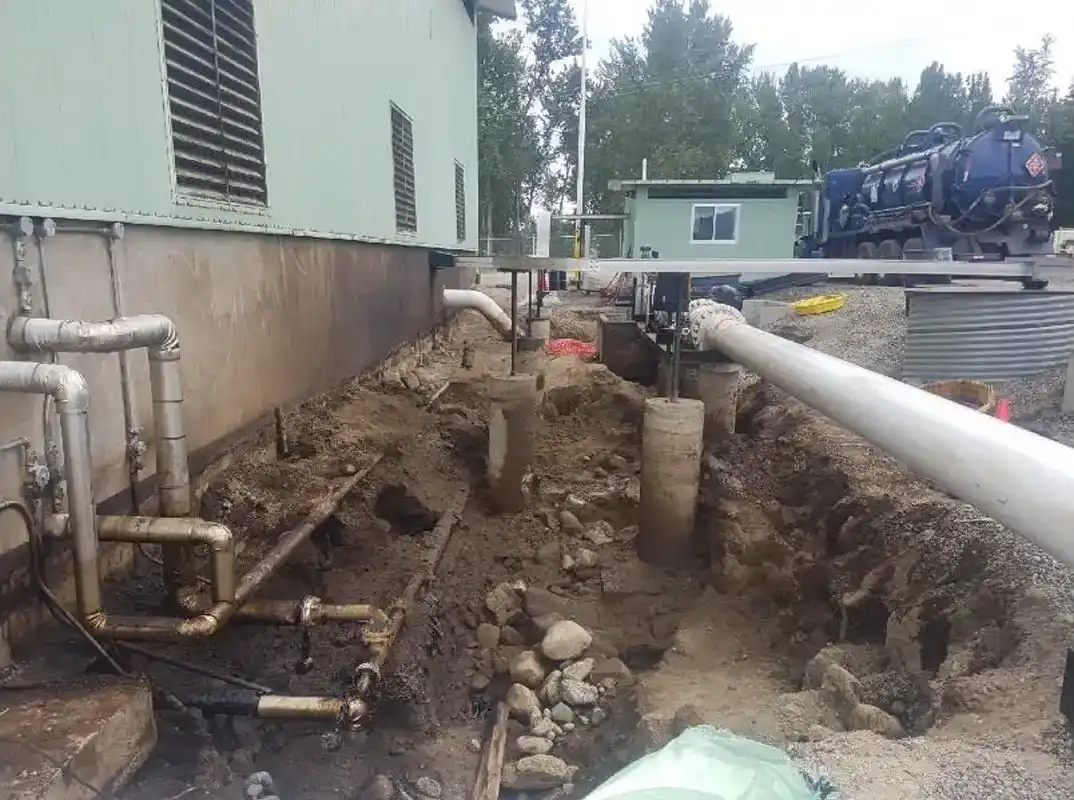
II. Design
Based on the mass of contaminant, a nutrient addition to achieve an approximate C:N:P balance of 100:10:1 was calculated, and approximately 284 kg of nitrogen and 28 kg of phosphorus were deemed required. To achieve the nitrogen dose requirements, 3,053 kg of Chemco Oxydor 60 was applied. Oxydor 60 is a liquid nitrate fertilizer consisting of 60% active ingredient. The phosphorus Figure 1 – Release location and residual staining following initial hydrovac response efforts. requirement was met using 1,670 kg of the Chemco MKP 7.5 % + AMP (phosphate mix). For the bio stimulation component, 30 kg of Chemco’s BCP 35s microbe amendment was recommended and applied. The nutrients and BCP 35s were diluted in non-chlorinated water and mixed prior to injection. Potential challenges for this site included the possible toxicity associated with the higher petroleum hydrocarbon concentrations, as well as moisture, pH, and temperature conditions at the site. It was also noted that a constraint to biodegradation could be low solubility of the heavier molecular weight hydrocarbons. A surfactant was considered to augment solubility and thus bioavailability, however the concern of mobilization and migration of the contaminants into the water table resulted in this option not being selected.